Looking for ways to file a tax return in Sage 50 then you’re landed on the right page? On the other hand, some taxpayers get a head start and file their returns on the first day of the new tax year. If you have not done yet then don’t worry. If you use Sage 50 software, this article will walk you through the entire tax filing process. We’ll also go over the specifics of deadlines, fines, and permissible expenditures while also taking a look at the reasons why so many companies need accountants.
Need Expert Help: Are you getting File a Tax Return in Sage 50 and don’t know how to solve it? In that case, you must get immediate help from our Sage 50 experts by dialing the ReConcileBooks helpline number +1347-967-4079 at any time.
Why Do You Need to File a Tax Return in Sage 50?

Tax is often routinely withheld at the source from pay and pensions for employees and pensioners. However, individuals and organizations must file a Self Assessment tax return if their other income is greater than a particular threshold and is not deducted at source.
You must submit a tax return if you earned more than £1,000 while operating as a sole proprietor during the most recent tax year (6 April 2021 to 5 April 2022). If you were a director of a limited company or a partner in a commercial partnership whose income was not taxed at source and/or owe additional tax, you must also file one.
If you have any specific query, also get in touch with the experts of Sage 50 live chat 24×7 helpdesk.
You could still be required to file a return even if your principal source of income is your pay or pension if you work in certain industries, received a PAYE salary of more than £100,000, or get any other untaxed income, such as from:
- Tips and commission
- Foreign income
- Renting
- Savings, investments and dividends.
Additionally, you can submit a tax return online to request income tax relief or to demonstrate your self-employment, for instance, to qualify for maternity or tax-free childcare.
If you’re still unsure if you need to file a return, HMRC provides you this decision tree.
Tax Return Dates and Deadlines
If you are self-employed or a sole proprietor, the deadline to register for Self Assessment for the most recent tax year was October 5, 2022. Paper tax returns have to be submitted by October 31, 2022, at midnight. The online submission cut-off is January 31, 2023, at midnight.
Suggested Reading: Sage Digital Tax for Vat
You may need to make two payments toward your impending tax bill for the current tax year after filing your first tax return, in addition to any tax and National Insurance (NI) that is owed for the prior tax year. You’ll need to do this every year going forward; it’s referred to as Sage 50 account tax codes.
The only exceptions to this rule are if your most recent Self Assessment tax bill was less than £1000 or if you have already paid more than 80% of all source tax due in the preceding year (note that underpaid tax collected via PAYE in the following year also counts as being deducted at source).
The initial deadline for making the first account-based payment is also midnight on January 31, and midnight on July 31, respectively.
How to Register and File a Tax Return Online?
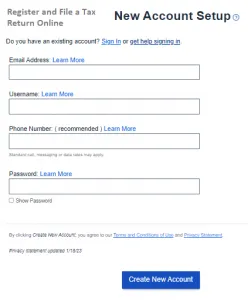
According to HMRC, over 93% of individuals file their tax returns online because it is quick, secure, and accessible around-the-clock. You may also sign up for email notifications and online messaging to assist you in managing your tax affairs.
You must sign up for an HMRC online account if you haven’t filed a tax return online previously.
After you sign up, HMRC will mail you an activation number. Since it may take up to 21 days to arrive if you’re abroad or 10 working days if you’re at home, be sure to sign up well in advance. Additionally, you’ll get a user ID and a Unique Taxpayer Reference (UTR).
If you have previously submitted a return but not for the previous year, you must re-register.
Get all the information you require in advance before submitting your Self Assessment application online.
You will require your UTR, National Insurance number, and, if available, an employer reference. You could require your P60 end-of-year certificate, P11D benefits or expenses, P45 information about quitting your job, paystubs, and/or your P2 PAYE coding notice.
Suggested Reading: Fica Tax and Tax Withholding Work in 2021 2022
You’re now prepared to take on the actual online form. (If you want to get acquainted with the sections and data you’ll probably need to provide, here is the printed form’s pdf version.)
You must have your bank or building society statements on hand, and if you are self-employed, you may also require your profit and loss statement or other financial data.
- The first section requests personal information. The next inquiry concerns the sources of your income or gains, such as work or self-employment, businesses or partnerships, real estate, trusts, capital gains, or sources in the UK or abroad.
- If you did get money from any of the boxes in this section, check the corresponding one. This will lead to further inquiries regarding various income sources emerging.
- The third section inquires about income from pensions, share dividends, interest from banks or building societies, and benefits. Even if you’re conducting a Self Assessment because you’re a lone proprietor, it’s crucial to indicate these. No matter where your revenue originates from, HMRC must be informed.
- The next section of the form requests additional information, including student loan information, pension payments, gifts, charitable donations, child benefit information, and marital allowances.
Allowable Expenses
You will incur a variety of operating expenses if you are self-employed. As long as these charges qualify as permitted expenses, you can deduct some of them from your taxable earnings.
These can include:
- Operating expenses for an office, such as phone or stationery costs.
- Uniforms or protective gear are normally not eligible for reimbursement, but, you may be able to claim shoes or business-casual apparel.
- Salary or subcontractor costs are examples of staff expenses.
- Such as insurance premiums or bank fees, are financial costs.
- The sum of some or all fees paid to consultants like accountants or attorneys.
- Business rates, heating, lighting, and other expenses related to your office space.
- Website costs such as those associated with marketing or advertising, but not expenses related to entertaining clients, including lunch purchases.
HMRC’s online filing system will determine your tax liability, according to Charlie Walker, a partner at Tax Assist Accountants in Bedford, but it won’t verify that your statistics are accurate or that you have claimed all of your allowed costs, reliefs, and allowances.
Allowances include a wide range of topics, he asserts. “Research and development, using your home as an office within specific parameters, purchasing structures for company purposes, as well as travel and lodging when working away from your home are a few of the frequent or large deductions and exemptions.
“Capital allowances, like as spending on business equipment, should not be overlooked. Many capital allowances for SMEs, including those for equipment and machinery, give up to 100% tax savings thanks to the annual investment allowance.
An alternative to claiming individual costs You might be able to claim simplified expenditures, which are set rates you can use to figure out tax savings on things like cars, working from home, and residing on your business’s property.
Although it saves time, doing so can prevent you from claiming all of the available benefits.
Another option is to use the trade allowance in place of expenses to lower your tax liability. The government permits sole proprietors to claim up to £1,000 as a tax-free trading allowance; however, if you use it, you are not permitted to claim expenditures.
Charity Donations on Tax Returns
You can receive tax benefits for contributions made by individuals to charities or community amateur sports clubs (CASCs), so be careful to mention all charitable contributions in your return.

Whether you give through Gift Aid, directly from your salary or pension through a Payroll Giving program, give land, property, or shares, or make a bequest, the tax benefit is either given to you or the charity.
Due to the fact that limited corporations pay less corporation tax when they donate to charity, there are various restrictions for them. You must maintain a record of your gifts in order to be eligible for tax relief.
Penalties for Filing Late and Appeals
If you submit your paperwork after the deadline or make your payment late, you’ll typically have to pay the penalty. On the other hand, if you have a good reason, you can contest a penalty.
If you file your tax return or pay your tax bill after three months have passed, you could be subject to a £100 fine. If you wait until the last minute, you will have to pay extra, and HMRC will add interest.
A more intricate system of sanctions based on daily penalties and so-called tax gear penalties is in place for violations lasting longer than three months. A tool for estimating penalties is also available from HMRC.
An accountant or tax advisor may be able to file your return for you using their special agent logins with HMRC, according to Charlie Walker, if you are preparing your tax return and are concerned that your online access to the HMRC website won’t be functioning in time to file before January 31.
Nick Levine continues, “Filing late also raises the likelihood that HMRC will examine your return more closely. So, fill out the form as soon as you can to minimise tension and missing the deadline. Contact [HMRC] right away if you anticipate missing a tax payment deadline. You might be granted more time to pay or the option to make one-time or recurring payments. Remember that as January 31 draws closer, both tax advisors and the online service become busier.
Ways to Pay
You can pay your taxes using online or telephone banking (faster payments), CHAPS, corporate or debit cards used online, your bank or building society, BACS, direct debit (if you’ve previously set one up with HMRC), or postal checks and checks.
The Post Office is no longer a place to make payments.
More information about each choice is available in Pay Your Self Assessment Tax Bill.
Unless you are paying with quicker payments or by debit or credit card, make sure your payment reaches HMRC on the final working day prior to the deadline if the deadline occurs on a weekend or a holiday.
Charlie Walker advises, “Make sure you set aside money each month to cover your tax obligation, especially if this is your first year working for yourself. We advise saving aside a quarter of your profits for taxes as a general rule. Increase that to a third if you pay tax at a higher rate.
For the money, you can decide to open a different savings account. Additionally, any interest is yours to keep.
Suggested Reading: Sage 50 payroll employee licence
Why and How Much an Accountant Charges, for Business Owners
The biggest benefit of filing a tax return is the cost savings on accounting expenses. However, many business owners find that hiring an accountant rapidly pays for themselves since they are either too busy to do it themselves or don’t fully grasp the many allowances they might claim.
According to Chas Roy-Chowdhury, head of taxation at the Association of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA), “People can get themselves into trouble if they try to save money by taking short cuts. The cost of hiring an accountant should be reduced through tax savings and the avoidance of errors and fines.
Using an accountant is an excellent approach to make sure you are up to date because tax laws change frequently. Additionally, professionally qualified accountants must adhere to rules of conduct and ethics and meet standards for ongoing professional development. You will also have redress if something goes wrong.
To make sure you are paying the right amount for an accountant, Chas advises comparison shopping. For a small to medium-sized practise, the normal rate would be between £100 and £200 per hour.
Suggested Reading: Reconcile Vat Return in Sage 50
The location of the company and the difficulty of the work may also affect fees. For a simple tax return, a smaller accountant might bill between £250 and £300.
It is appropriate that the accountant will know whether this is permissible, but sole proprietors and other self-employed people may be able to deduct the charges of their accountant as an expense.
The accountant must “wholly and entirely” determine the amount of tax due on the self-employed income for it to be considered acceptable, even though it is technically not permitted.
The accountant can decide that it’s not a permissible expense or that only a portion of their fees can be claimed if the Self Assessment includes computations for any other income (such capital gains).
Conclusion
Well, this article will provide you with a deep understanding of how to file taxes in year 2022- complete tax filing guide. Hopefully, reading this segment will surely work for you to File a Tax Return in Sage 50. Get a better grip on this particular topic by going through this segment with full concentration. Or connect LIVE CHAT with Professionals using our Sage Helpdesk Customer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q. How Do I Modify an Existing Tax Code in Sage 50?
Ans. The below steps helps you to modify an existing tax code in Sage 50:
- Click Settings in the Home window’s Setup menu
- Choose Tax Codes under Company, then click Sales Taxes
- By clicking the Description column and entering a new description, you can modify the tax code description that appears on your forms
- By selecting All journals, Purchases, or Revenues from the list under the Utilize In column’s Search Finder button, you can modify which transactions use this tax code
- The Settings window can be closed by clicking on the Ok tab.
Q. How to Remove an Existing Tax Code in Sage 50?
Ans. You can remove an existing tax code in Sage 50:
- Click Settings in the Home window’s Setup menu
- Choose Tax Codes under Company, then click on the “Sales Taxes in Sage 50” option
- You can delete a tax code by selecting it in the Code column and pressing the Delete key
- The Settings window can be closed by clicking on the Ok tab.
Q. What are VAT Tax Codes in Sage 50?
Ans. Sage tax codes are added to transactions in Sage accounting software so that you can accurately compute VAT tax returns. The codes are applied when publishing sales or purchase transactions in Sage 50cloud Accounts and Sage 50 Accounts.
